What is an APT Mirror Local Repository?
An APT Mirror Local Repository is a local copy of software package repositories from a remote server, used in Debian-based systems like Ubuntu. It allows client machines to download packages from a local server instead of relying on external sources, improving download speed and reducing internet bandwidth usage. A local mirror also enables offline package installations and updates. It can be customized to mirror specific repositories or components like security updates or main packages. Setting up an APT mirror is beneficial in environments with multiple systems or where network reliability or bandwidth is a concern.
Why do we need a Mirror Local Repository?
A Mirror Local Repository is essential for improving software management in environments with multiple systems or limited internet access. It enables faster package downloads by providing a local source, reducing reliance on external servers and minimizing internet bandwidth usage. This is particularly beneficial in large organizations or remote locations with unreliable or slow internet connections. A local mirror also allows for offline updates and installations, ensuring system maintenance even when the internet is unavailable. Furthermore, it offers better control over updates, allowing customization to mirror only specific repositories or components, such as security updates or essential packages.
What is APT-Mirror?
APT-Mirror is a tool used for creating and managing local mirrors of APT (Advanced Package Tool) repositories. It is typically used in Debian-based systems like Ubuntu to download and store entire software repositories locally. By doing so, it allows administrators to set up a local copy of the repository that can be accessed by other machines on the same network.
APT-Mirror helps reduce bandwidth usage, speeds up package downloads, and allows offline installations or updates. It also offers greater control over the packages and versions being served to client systems, making it ideal for environments with many machines or slow internet connections.
How to set it up?
Preparation
- Server: Ubuntu 20.04, 2 CPU, 4GB Ram, 100GB Disk
- Client: Ubuntu 18.04, 2 CPU, 2 GB RAM, 20GB Disk
Step 1: Update System and Install Dependencies
Update the package list:
sudo apt updateInstall Nginx to serve the mirror
sudo apt install -y nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx sudo systemctl start nginxNginx will serve the mirrored repository files over HTTP.
Create a directory for the mirror
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/ubuntuNote: This is where the mirrored repository files will be stored.
Step 2: Install apt-mirror
Install the apt-mirror package, which downloads repository files and creates a local mirror:
sudo apt install -y apt-mirrorStep 3: Backup and Configure apt-mirror
Backup the default configuration file
sudo cp /etc/apt/mirror.list /etc/apt/mirror.list-bakEdit the configuration file
Open the file: sudo nano /etc/apt/mirror.list
Modify the configuration: Replace or add the following lines:
############# config ##################
#
# set base_path /var/spool/apt-mirror
#
# set mirror_path $base_path/mirror
# set skel_path $base_path/skel
# set var_path $base_path/var
# set cleanscript $var_path/clean.sh
# set defaultarch <running host architecture>
# set postmirror_script $var_path/postmirror.sh
# set run_postmirror 0
set nthreads 20
set _tilde 0
#
############# end config ##############
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic main
clean http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu
Note:
set base_path: Specifies the directory for storing mirror files.set nthreads: Number of threads used for downloading files.debURLs: Specify the repositories and components to mirror.clean: Cleans old or unnecessary files from the local mirror.- Save and close the file.
Step 4: Run apt-mirror to Start Mirroring
Run the apt-mirror command to download repository files:
sudo apt-mirror
- This process can take a long time, depending on your internet speed and the size of the selected repositories.
- Check progress by reviewing the log:
tail -f /var/log/apt-mirror.log
Step 5: Configure Nginx to Serve the Mirror
Open the Nginx configuration file
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultModify the configuration to serve the mirrored files
Add or replace the server block with the following
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
root /var/www/html/ubuntu;
index index.html index.htm;
location / {
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
autoindex_localtime on;
}
# Optional: Restrict access to specific IPs
# allow 192.168.0.0/16; # Allow access from a specific network
# deny all;
}- Save and close the file.
Test the Nginx configuration
sudo nginx -tReload Nginx to apply the changes
sudo systemctl reload nginxStep 6: Verify the Repository
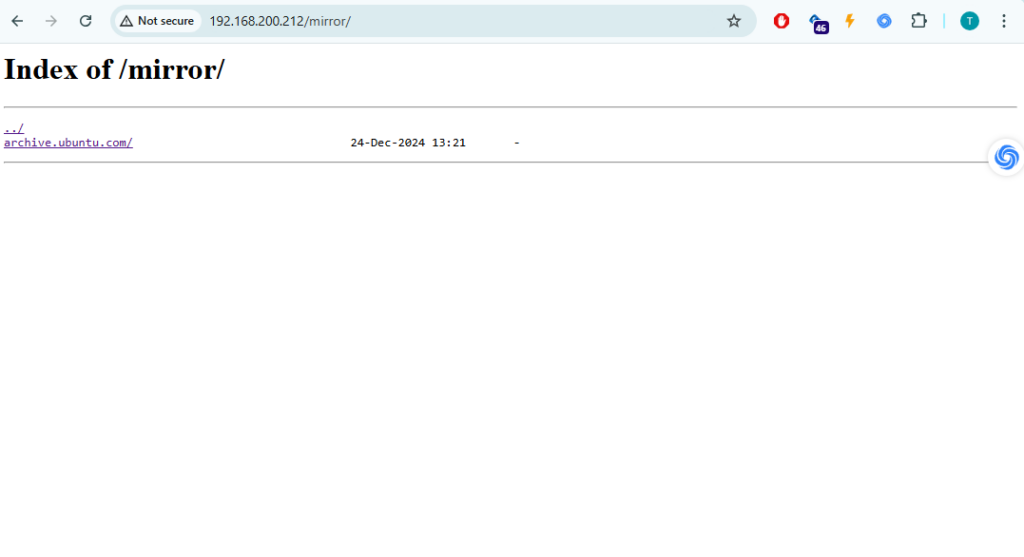
Open a web browser and visit: http://<your-server-IP>/mirror/archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/
You should see the directories and files of the mirrored repository.
Step 7: Configure Client Machines
Add the local mirror to the client’s sources list
echo "deb http://<your-server-IP>/mirror/archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic main restricted universe multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/local-mirror.list
echo "deb http://<your-server-IP>/mirror/archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/local-mirror.list
echo "deb http://<your-server-IP>/mirror/archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/local-mirror.list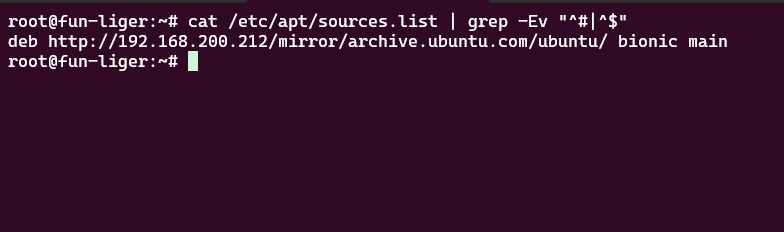
Install packages from the local mirror
sudo apt update
sudo apt install <package-name>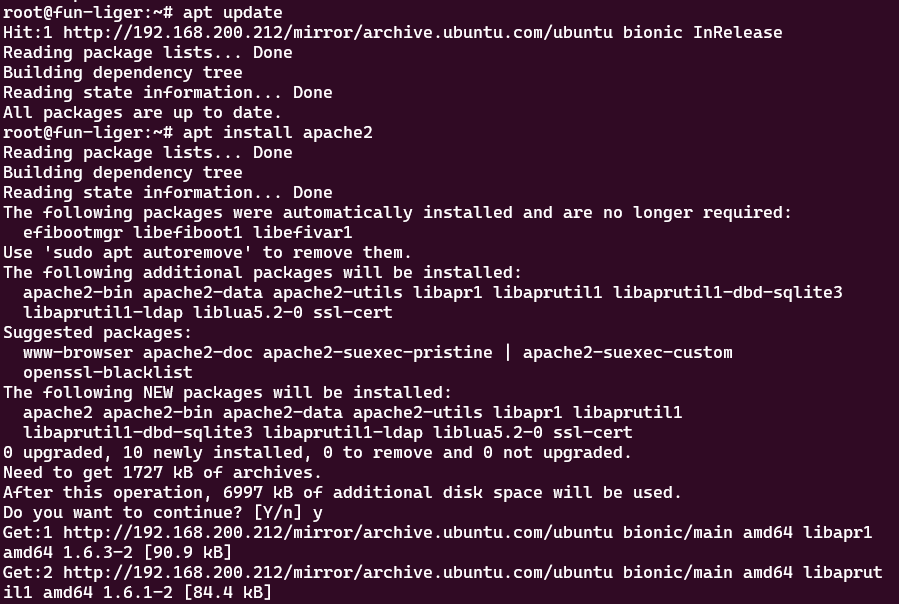
Step 8: Automate Mirror Updates
To keep the mirror up to date, schedule regular updates using cron:
- Open the crontab:
crontab -e
- Add the following line to update the mirror daily at 2 AM:
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/apt-mirror > /var/log/apt-mirror.log
Notes
- Disk Space: Ensure your server has enough space (100 GB or more) to store the mirrored repository.
- Access Control: To restrict access, modify the Nginx configuration using IP whitelisting or authentication.
- Performance Optimization:
- Increase
set nthreadsin/etc/apt/mirror.listfor faster downloads. - Use a high-performance server with good network connectivity.
- Increase


Leave a Reply